拉取镜像
1 | docker pull mysql |
启动指令
1 | 简单启动 |
1 | 常用 |
1 | docker pull mysql |
1 | 简单启动 |
1 | 常用 |
A load word or store word instruction uses only one memory address. The lowest address of the four bytes is used for the address of a block of four contiguous bytes.
How is a 32-bit pattern held in the four bytes of memory? There are 32 bits in the four bytes and 32 bits in the pattern, but a choice has to be made about which byte of memory gets what part of the pattern. There are two ways that computers commonly do this:
Big Endian Byte Order: The most significant byte (the “big end”) of the data is placed at the byte with the lowest address. The rest of the data is placed in order in the next three bytes in memory.
Little Endian Byte Order: The least significant byte (the “little end”) of the data is placed at the byte with the lowest address. The rest of the data is placed in order in the next three bytes in memory.
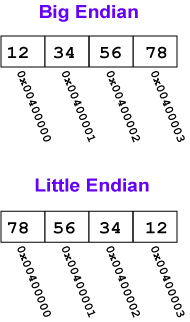
In these definitions, the data, a 32-bit pattern, is regarded as a 32-bit unsigned integer. The “most significant” byte is the one for the largest powers of two: 231, …, 224. The “least significant” byte is the one for the smallest powers of two: 27, …, 20.
For example, say that the 32-bit pattern 0x12345678 is stored at address 0x00400000. The most significant byte is 0x12; the least significant is 0x78.
Within a byte the order of the bits is the same for all computers (no matter how the bytes themselves are arranged).
字节序,也就是字节的顺序,指的是多字节的数据在内存中的存放顺序。
在几乎所有的机器上,多字节对象都被存储为连续的字节序列。例如:如果C/C++中的一个int型变量 a 的起始地址是&a = 0x100,那么 a 的四个字节将被存储在存储器的0x100, 0x101, 0x102, 0x103位置。
根据整数 a 在连续的 4 byte 内存中的存储顺序,字节序被分为大端序(Big Endian) 与 小端序(Little Endian)两类。 然后就牵涉出两大CPU派系:
另外,还有一些处理器像ARM, DEC Alpha的字节序是可配置的。
那么,到底什么是大端,什么是小端? 如下图:
我相信上面的图已经够直观了。也就是说:
各自的优势:
如果你写的程序只在单机环境下面运行,并且不和别人的程序打交道,那么你完全可以忽略字节序的存在。
但是,如果你的程序要跟别人的程序产生交互呢? 比如,当一个 C/C++ 的程序要与一个 Java 程序交互时:
试想,如果你的C/C++程序将变量 a = 0x12345678 的首地址传递给了Java程序,由于Java采取 Big Endian 方式存储数据,很自然的它会将你的数据翻译为 0x78563412。显然,问题就出现了!!!
另外,网络传输一般采用 Big Endian,也被称之为网络字节序,或网络序。当两台采用不同字节序的主机通信时,在发送数据之前都必须经过字节序的转换成为网络字节序后再进行传输。
由于 C/C++ 存储数据时的字节序依赖所在平台的CPU,所以我们可以通过C/C++程序判定机器的端序:
1 | void Endianness() |
网络字节序:TCP/IP各层协议将字节序定义为 Big Endian,因此TCP/IP协议中使用的字节序是大端序。
主机字节序:整数在内存中存储的顺序,现在 Little Endian 比较普遍。(不同的 CPU 有不同的字节序)
在进行网络通信时 通常需要调用相应的函数进行主机序和网络序的转换。Berkeley socket API 定义了一组转换函数,用于16和32bit整数在网络序和本机字节序之间的转换。htonl,htons用于本机序转换到网络序;ntohl,ntohs用于网络序转换到本机序。
1 | -a或--all:显示所有连线中的Socket; |
1 | netstat -a #列出所有端口 |
1 | -t<表>:指定要操纵的表; |
1 | iptables -t 表名 <-A/I/D/R> 规则链名 [规则号] <-i/o 网卡名> -p 协议名 <-s 源IP/源子网> --sport 源端口 <-d 目标IP/目标子网> --dport 目标端口 -j 动作 |
1 | iptables -F |
1 | iptables -A INPUT -s 127.0.0.1 -d 127.0.0.1 -j ACCEPT #允许本地回环接口(即运行本机访问本机) |
1 | sudo iptables -I FORWARD -p tcp --dport 8080 -j DROP # 不响应对8080的请求,等待超时(效果:Operation timed out) |
灰度测试在系统重构过程中是必不可少的,很多公司有自己的灰度解决方案。对于初创型或者小型团队,缺少必要的工具,因此这里借用nginx的转发(反向代理)能力做一下灰度测试。
在nginx中配置proxy_pass代理转发时,如果在proxy_pass后面的url加/,表示绝对根路径;如果没有/,表示相对路径,把匹配的路径部分也给代理走。
假设下面四种情况分别用 http://192.168.1.1/proxy/test.html 进行访问。
CASE 1:
1 | location /proxy/ { |
代理到URL:http://127.0.0.1/test.html
CASE 2:
1 | location /proxy/ { |
代理到URL:http://127.0.0.1/proxy/test.html
CASE 3:
1 | location /proxy/ { |
代理到URL:http://127.0.0.1/v1/test.html
CASE 4:
1 | location /proxy/ { |
代理到URL:http://127.0.0.1/v1test.html
1 | location /api_to_gray { |
1 | location /api_to_gray { |
1 | comm [-123][--help][--version][第1个文件][第2个文件] |
参数:
需要排序,即便排序也不一定正确,所以不建议使用,适合对比极少数同行差异的文件。
同comm指令,也是逐行对比,如果同样的内容处于不同行中,对比结果也不是期望的
1 | diff [-abBcdefHilnNpPqrstTuvwy][-<行数>][-C <行数>][-D <巨集名称>][-I <字符或字符串>][-S <文件>][-W <宽度>][-x <文件或目录>][-X <文件>][--help][--left-column][--suppress-common-line][文件或目录1][文件或目录2] |
1 | grep [-abcEFGhHilLnqrsvVwxy][-A<显示列数>][-B<显示列数>][-C<显示列数>][-d<进行动作>][-e<范本样式>][-f<范本文件>][--help][范本样式][文件或目录...] |
1 | 查看file2比file1多出的内容 |
-x –line-regexp : 只显示全列符合的列。
-f <规则文件> 或 –file=<规则文件>: 指定规则文件,其内容含有一个或多个规则样式,让grep查找符合规则条件的文件内容,格式为每行一个规则样式。
1 | $args //请求中的的参数名,即“?”后面的arg_name=arg_value形式的arg_name |
主要位于org.apache.ibatis.binding包里面
1 | MapperRegistry 负责注册获取Mapper |

org.apache.ibatis.session.defaults.DefaultSqlSession#getMapper
2
3
4
5
---> Configuration.getMapper
---> MapperRegistry.getMapper
---> mapperProxyFactory.newInstance
---> Proxy.newProxyInstance
command 来自 mapper的注解或者xml配置
1 | // org.apache.ibatis.binding.MapperMethod#execute |
1 | └── org |
1 | ├── BaseExecutor.java |
1 | ├── AutoMappingBehavior.java |
org.apache.ibatis.transaction.jdbc.JdbcTransaction#openConnection
1 | T org.apache.ibatis.session.defaults.DefaultSqlSession#getMapper |
1 | at org.apache.ibatis.transaction.jdbc.JdbcTransaction.getConnection(JdbcTransaction.java:60) |
1 | org.apache.ibatis.executor.CachingExecutor#query(ms,parameterObject,rowBounds,resultHandler) |
Executor ==> Statement ==> Parameter ==> ResultSet
绿色 几个组件都是可以通过mybatis插件改写的,参考 mybatis plugin
Executor (update, query, flushStatements, commit, rollback, getTransaction, close, isClosed)
StatementHandler (prepare, parameterize, batch, update, query)
ParameterHandler (getParameterObject, setParameters)
ResultSetHandler (handleResultSets, handleOutputParameters)
yum install -y wireshark
1 | sudo tcpdump -A -s 0 'tcp port 8080 and (((ip[2:2] - ((ip[0]&0xf)<<2)) - ((tcp[12]&0xf0)>>2)) != 0)' |
1 | 加 -V 显示包体内容,否则仅url,response_code等 |
1 | sudo tcpdump -i any -s 0 -l -w - dst port 3306 | strings | perl -e ' |
1 | time_delta 本次回包耗时(RTT) |
译自 A tcpdump Tutorial and Primer with Examples 有所增删,可以通过 man tcpdump 获取更详细信息
只要和网络沾边,都可以使用tcpdump来排查问题。
-i any :监听任意网络设备-i eth0 :监听eth0-D :列出所有可监听设备-n :不要把IP解析为主机名(显示IP)-nn :不要把IP和PORT解析为主机名和服务(显示IP和端口)-q :显示更少信息-tttt :更具有可读性的时间格式-X :以hex和ascii格式显示包内容-XX :同 -X , 同时包含以太网协议头-v, -vv, -vvv :显示更多信息-c x :最多抓取x个包,然后退出-A :以ASCII格式打印每个包(最小化link level的头),适合抓web页面-s :Define the snaplength (size) of the capture in bytes. 使用 -s0 获取全部-w file :把结果输出到文件file-S :Print absolute sequence numbers.表达式用于过滤抓到的包,有三类表达式
host net portsrc dsttcp udp icmp 等tcpdump -i any 当机器有多个网卡,不确定流量走哪个时,使用这个选项
1 | tcpdump -i eth0 |
1 | tcpdump -nn -tttt -vv -S -c 10 |
1 | tcpdump port 80 and host 10.129.204.105 |
1 | tcpdump -nn -v -X -s0 -c 1 tcp |
获取所有目标端口是80的流量 tcpdump -i any -nn -s0 -c 10 -A tcp and dst port 80
获取所有80端口的流量 tcpdump -i any -nn -s0 -c 10 -A tcp and port 80
获取vrrp协议的流量,用于调试keepalive tcpdump vrrp
1 | tcpdump ip6 |
1 | tcpdump -nn portrange 21-23 and src host 10.136.110.179 |
1 | tcpdump -i any -nn port 80 and less 80 |
通过 and 或 && or 或 || not 或 ! 可以组合表达式
表达式的结合律有点奇怪,需要自己体会,例如: 监听80或8080并且来自10.129.204.105的请求 tcpdump -i any -nn -vv port 80 or 8080 and src host 10.129.204.105 tcpdump -i any -nn -vv port 80 or port 8080 and src host 10.129.204.105
监听80并且来自10.129.204.105的请求或监听8080的请求(没有来源IP限制) tcpdump -i any -nn -vv port 80 and src host 10.129.204.105 or port 8080
为了避免这些微妙的差别,可以使用 () ,注意这里的单引号 tcpdump -i any -nn -vv '(port 80 or port 8080)' and src host 10.129.204.105
1 | tcpdump -i any -nn -vv port 80 and src host 10.129.204.105 |
1 | tcpdump -i any -nn dst host 10.136.110.179 and not tcp |
1 | tcpdump -i any -nn src host 10.129.204.105 and not dst port 22 |
先了解下TCP和IP协议头,虽然最后有0~40个可选bytes,这里没用到,可以先忽略它们。TCP头20bytes,其中tcp flags在第13个byte(下标为0) |C|E|U|A|P|R|S|F| 。
1 | TCP |
tcp[13] & 32 != 0 或 tcp[tcpflags] == tcp-urgtcp[13] & 16 != 0 或 tcp[tcpflags] == tcp-acktcp[13] & 8 != 0 或 tcp[tcpflags] == tcp-pshtcp[13] & 4 != 0 或 tcp[tcpflags] == tcp-rsttcp[13] & 2 != 0 或 tcp[tcpflags] == tcp-syntcp[13] & 1 != 0 或 tcp[tcpflags] == tcp-fin例如:获取所有SYN请求 tcpdump -i any -nn -A -s0 'tcp[13] & 2 != 0'
1 | tcpdump -i any -nn -s0 -X 'tcp[tcpflags] & (tcp-syn|tcp-fin) != 0' |
tcp[12] 的高4位是TCP HEADER的长度(通常是20 bytes),TCP之后是应用协议 0x47455420 是 GET 外加一个空格 tcpdump -i any -nn -s0 -X 'tcp[((tcp[12] & 0xf0) >> 2):4] = 0x47455420' 通常 tcpdump -i any -nn -s0 -X 'tcp[20:4] = 0x47455420' 也是可以的
1 | 0x5353482D` 是 `SSH-` `tcpdump -i any -nn -s0 -X 'tcp[20:4] = 0x5353482D' |
1 | ip[2:2]` 整个IP包的长度 `(ip[0] & 0xf) <<2` 是IP头的长度 `tcpdump -i any -nn -s0 -X port 80 and '(((ip[2:2] - ((ip[0]&0xf)<<2)) - ((tcp[12]&0xf0)>>2)) != 0)' |